
Have you ever wondered what is tonic solfa? Or maybe you have learned “do re mi fa so la ti do” instead of note names (C, D, E, etc.) and now you’d like to know how to translate between those two note naming systems?
In this step-by-step guide, I’d like to provide you with an easy explanation of solfa, how to use it, and how you can benefit from using it!
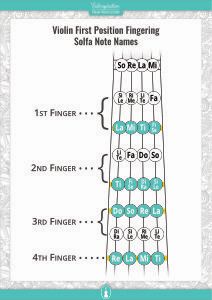
Violin First Position Fingering Chart
with Solfa Note Names
What is Tonic Solfa Notation?
Tonic solfa notation, also called Solfége, is a system of learning music where the tones are called do, re, mi, fa, so, la, ti. A hand gesture is assigned to each syllable. “Do” can be fixed to C4 (middle C) or moving and then always represent the base note (tonic) of each scale.
The solfa system puts the main focus on thinking about the relationship of musical notes to each other and to the tonic, so it is a great way to train your ears.
Tonic solfa was invented by Sarah Ann Glover from Norwich and further developed and popularized by John Curwen, after which it became known as the Curwen method.
It is called ‘tonic’ solfa, because (in the version with moving do) we label the tonic or base note of every key by the same name ‘do’.
What is “do re mi fa so la ti do”?
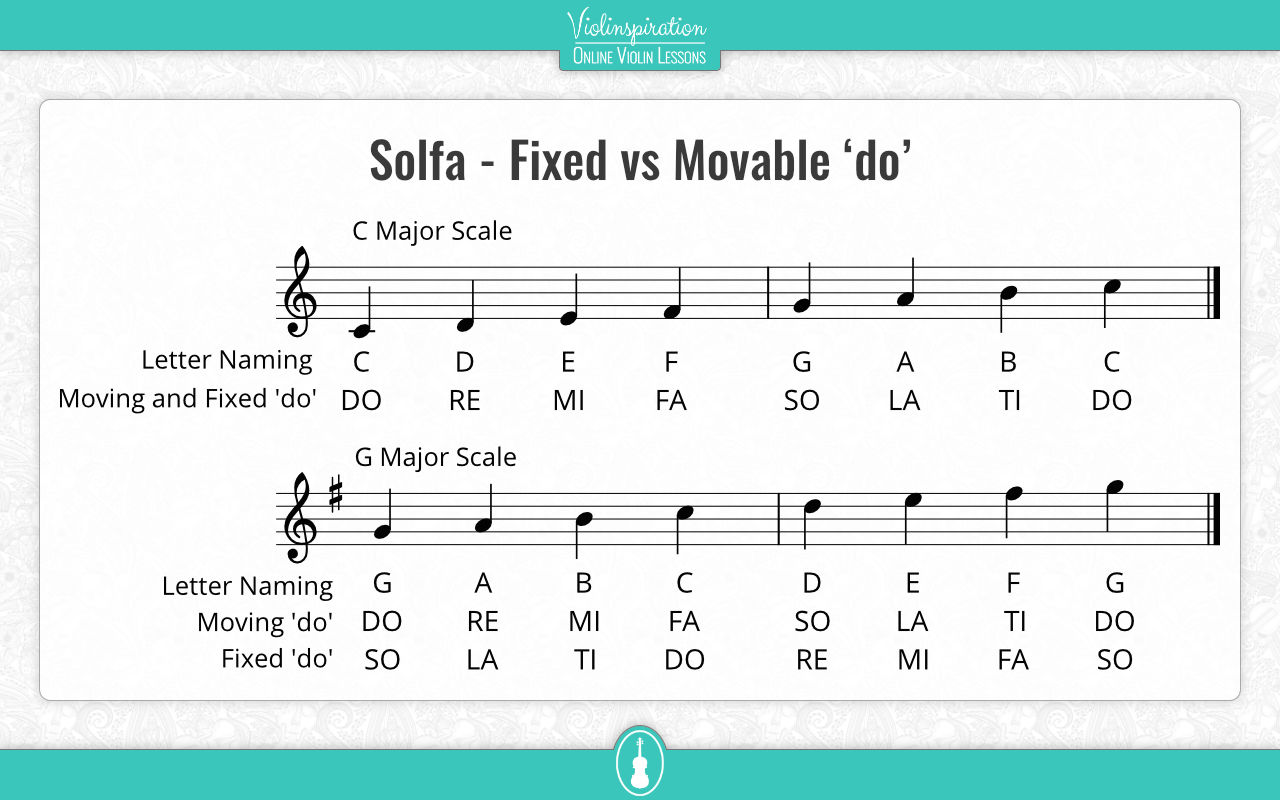
“Do re mi fa so la ti do” are the tonic solfa names of the notes in a major scale. The pitch of the notes depends on whether you’re using a fixed do or a movable do. Sometimes the ‘so’ is called ‘sol’.
Only in the case of the C Major scale, solfa note names correspond to the same pitch for every note.
What is Fixed “do”?
Fixed ‘do’ is when the note names “do re mi fa so la ti do” are used as a simple replacement for “C D E F G A B C”, which means that ‘do’ means exactly the same as ‘C’ (also called middle C or C3).
What is Movable “do”?
Movable ‘do’ is when the names ‘do re mi fa so la ti do’ refer to the relative position inside the scale (relative pitch). In this case, the ‘do’ will always be the first note of any scale.
The movable ‘do’ version of the solfa system is the predominant one in most of Northern and Central Europe.
How Solfa Works
Let’s analyze how to use solfa with moving do.
All major scales have the same whole step and half step structure (W W H W W W H). In solfa, these relationships are expressed by the names of the notes, which are do, re, mi, fa, so, la, ti, do.
The ‘do’ refers to the first note or tonic of a key. The ‘re’ to the second, the ‘so’ to the fifth, etc.
This relationship between the notes and their names stays the same, no matter what pitch we start the scale on. Instead of having to think about the names of the different notes in a scale, we can simply sing the scale by the solfa names, and this way we already know all major scales. We have learned it like a simple tune.
Scales Degrees in Solfa
In music theory, we have a term, scale degree, which refers to the position of a note within a scale. The first note is the tonic, then they are called supertonic, mediant, subdominant, dominant, submediant, subtonic, and tonic again.
| 1st note | Tonic | do |
| 2nd note | Supertonic | re |
| 3rd note | Mediant | mi |
| 4th note | Subdominant | fa |
| 5th note | Dominant | so |
| 6th note | Submediant | la |
| 7th note | Subtonic | si |
| 8th note | Tonic | do |
Instead of having to deal with these lengthy words, we can express the position of each note just by using their solfa name.
For example, when I say ‘so’, I am referring to the dominant, or when I say ‘la’ I mean the submediant or the 6th note. Please remember that it’s true only in the case of the movable do.
Accidentals and Chromatic Scales in Solfége
You might be wondering what happens to these names when we move outside of a major scale, or if we have some accidentals (sharps or flats) in a piece of music.
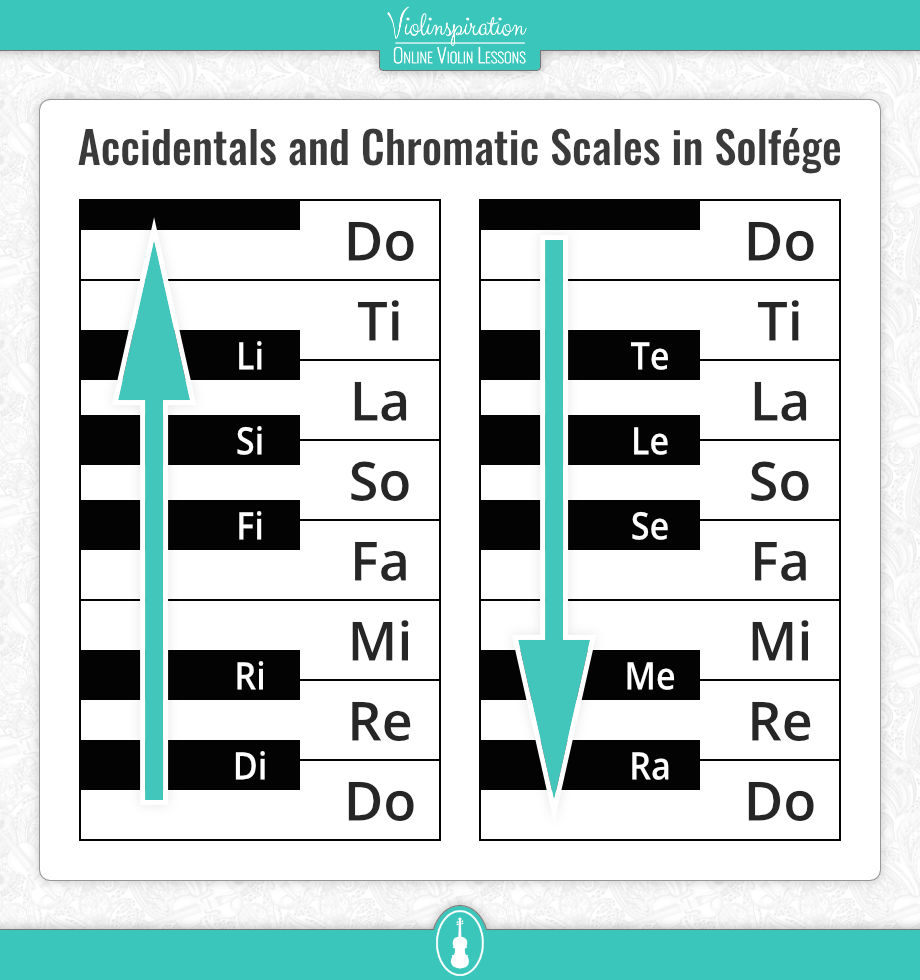
Each of the names in solfa can be modified up or down by a semitone or half step.
Going Up
Going upwards, or adding sharps, we alter the name of each by an ‘ee’ sound. So the chromatic scale becomes:
do, di, re, ri, mi, fa, fi, so, si, la, li, ti, do.
You will notice that the ‘me’ and the ‘ti’, both of which already end in an ‘ee’ sound, aren’t modified. This is for the simple reason that moving up a semitone from ‘me’ gives us a fa, which already has a name. Similarly, moving up from ‘ti’ by a semitone, we are already at ‘do’.
Although some people use these names for both going up and down, there’s a different modification of the solfa syllables when you go from higher pitch to lower.
Going Down
Moving down, that is adding flats to lower the pitch by a semitone, we have some options. It is good to pick one and stick to it, so after reading through this pick the version that you like best and use only that one.
Here are the three options I have come across:
- Use an ‘aw’ sound to get: do, ti, taw, la, law, so, saw, fa, me, maw, re, raw, do
- Use an ‘oo’ or ‘u’ sound to get: do, ti, tu, la, lu, so, su, fa, mi, mu, re, ru, do
- Or, as most people do, use an ‘e’ to get: do, ti, te, la, le, so, see, fa, mi, me, re, ra, do
Minor Keys
Relative Minor keys become really easy once you know how to use solfa. Simply starting on the ‘la’, you automatically have a natural minor scale. Modifying a couple of notes will give you the other minors.
Natural Minor
La ti do re mi fa so la – la so fa mi re do ti la
Harmonic minor
La to do re mi fa si la – la le fa mi re do ti la
Melodic Minor
La ti do re mi fi si la – la so fa mi re do ti la
Hand Symbols for Solfa
When children are taught tonic solfa, they are also taught hand symbols for each note. It is not essential to learn them to be able to use the system, but for the sake of completeness, I include it here.
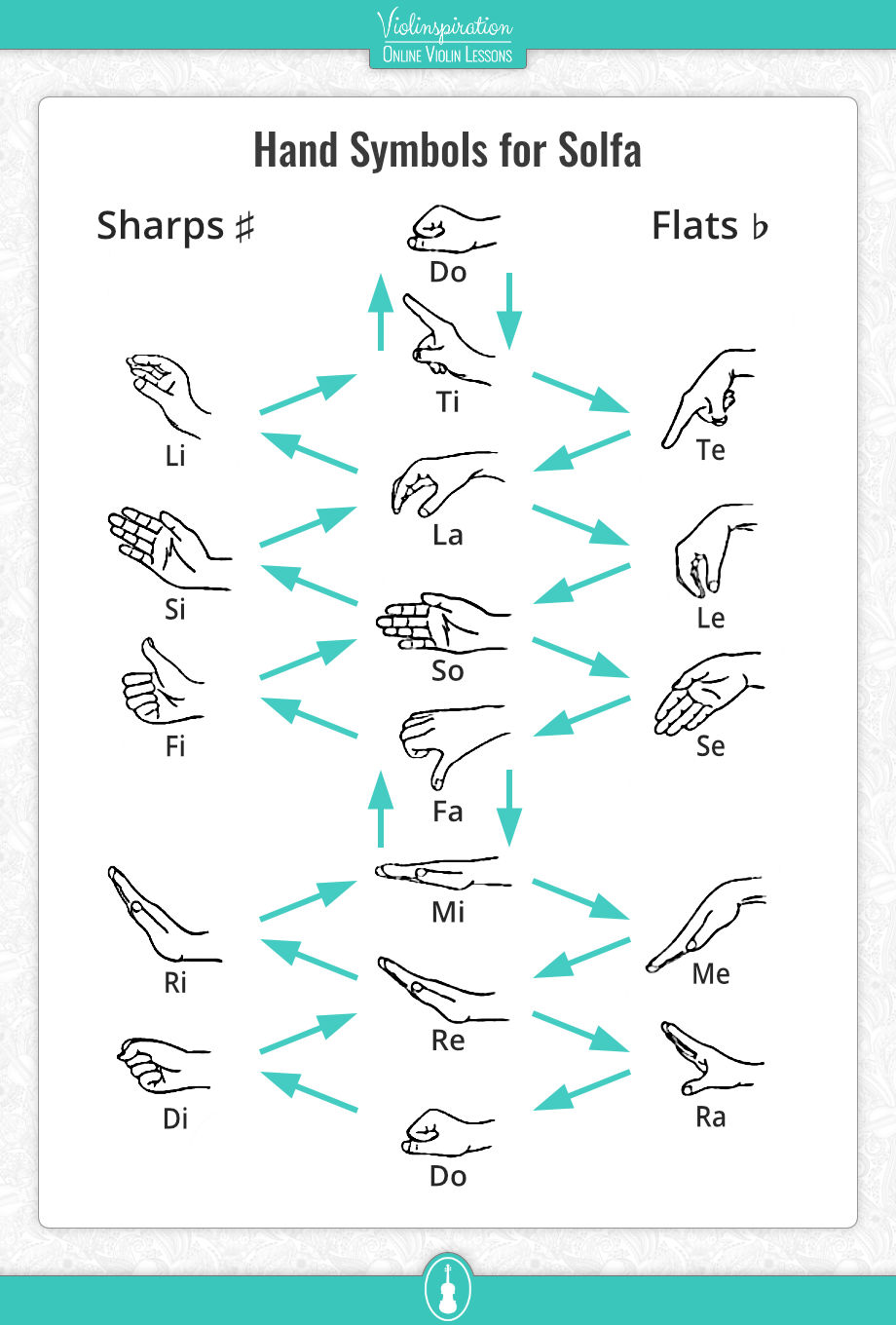
These hand signals can be used in choirs to indicate what note to sing next, or to reinforce learning for children with body movements.
How to Translate Between Note Names and Solfa
Translating between note names and solfa syllables is the easiest in the case of the C Major scale because the notes don’t have any accidentals (flats or sharps) in front of them. So C D E F G A B directly translates to do re mi fa so la ti.
Incidentally, this is where the fixed ‘do’ stops. But for those, who want to use a moving ‘do’, we can take the notes of any major scale and use the same names for its notes.
As an example let’s take a really complicated key signature, that of F# Major. This key has 6 sharps, and its notes are F#, G#, A#, B, C#, D#, E#, F#. In a fixed ‘do’ notation we would have to say fi si li ti di ri fa fi. However, with a moving ‘do’, we can simply call these notes by the familiar do, re, mi, fa, so, la, ti, do.
To translate a different type of scale, you need to identify first of all which note of the key signature it starts on, and then the positions of whole steps and half steps (tones and semitones) between consecutive notes. Once you’ve got this, you can lay the scale along the chromatic solfa scale as presented above, and copy the names.
Pieces with Do Re Mi
Let’s have a look at some easy pieces with solfa annotations.
Happy Birthday in Solfa
To figure out how to play (or sing!) Happy Birthday with tonic solfa names, we need to know that the song ends on the tonic note, therefore it is a ‘do’. Working backward we find that it in fact starts on a ‘so’. Here is the whole song for you:
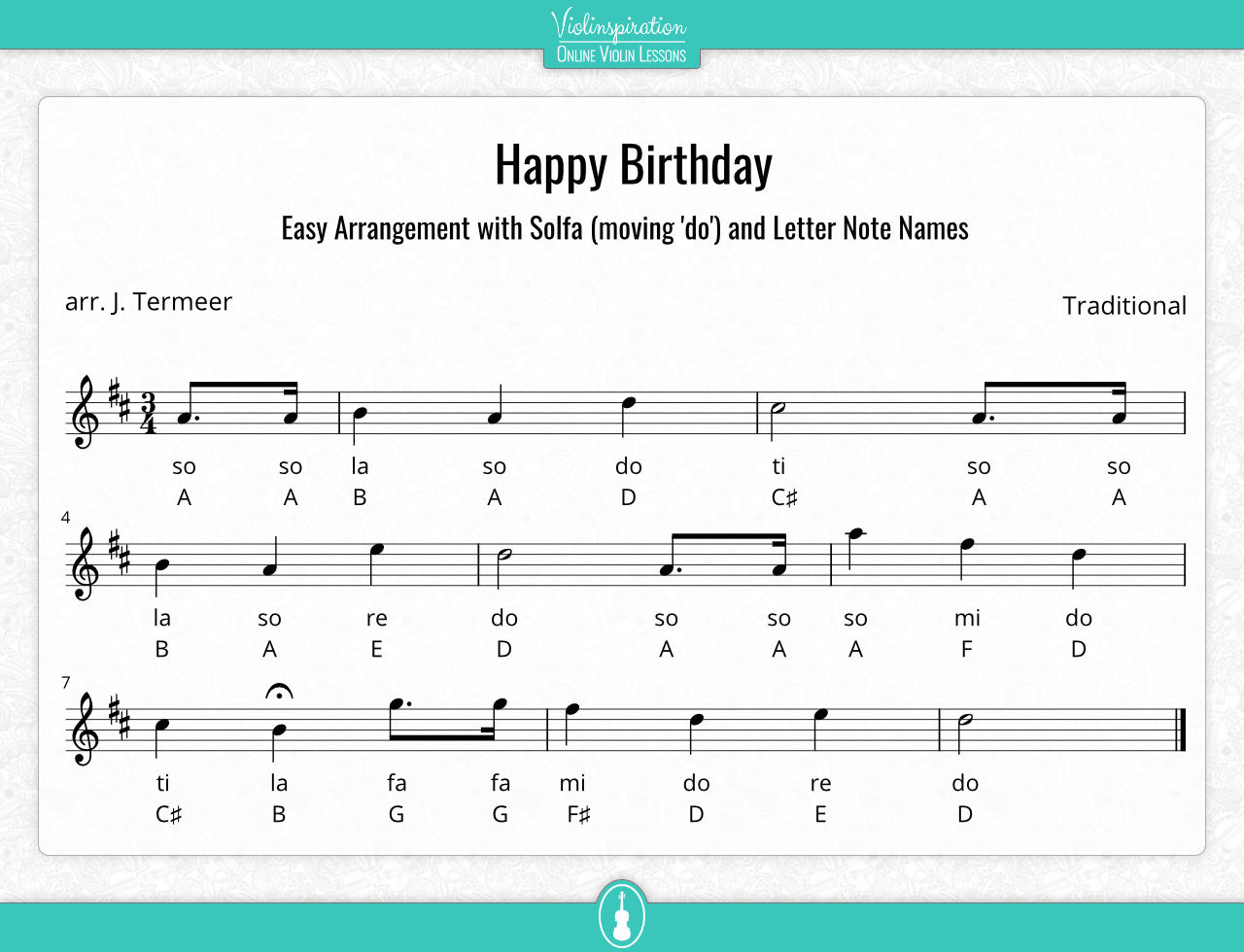

Happy Birthday in Solfa
The sound of music – Do Re Mi
There’s a very nice song from the musical The Sound of Music that teaches solfa a little bit. If solfa is totally new to you, make sure to watch the video below:
I hope this song helped you remember the syllables of solfa. Maybe you even tried to sing along? If you like this song, you can learn from my tutorial how to play it on your violin!
Add Solfa Syllables to Your Sheet Music with Musescore
Here’s a tip to Musescore users: using this free notation software, you can easily add solfa syllables to your score.
First, open the score or create new one. Then, right-click on staff and select Staff/Part Properties. Click on Advanced Style Properties. Next, choose your preferred option from the “Notehead scheme” dropdown list.
The feature shows the name of each note in various different systems, movable ‘do’ and fixed ‘do’, also letter names, and several other systems of notation.

Final Note
For someone with perfect pitch, whether we play a C or a D makes a big difference, because they can hear that these are totally different notes. For most people, however, transposing to a different key is more natural, and we can hear the melody of a scale before knowing the absolute frequency of its pitch.
This is very much like singing a song. You know the melody, but probably don’t remember the pitch where you have to start. In fact, we often just sing a song wherever we feel like starting, and it is still the same song.
This also means that once you know the structure of a scale, it doesn’t matter where you start, you can sing it, or play it. This is the same for all types of scales, once you know how they are made, you can sing them starting anywhere using the solfa names.
I would say that for a person who has perfect pitch, the solfa system may not be very useful, but for everyone else, it can make things simpler, especially if you’re just beginning to learn music.
If I should name a disadvantage of using solfa, it is a possibility that someone relies on this system so much that they don’t learn the letter names of notes.
Tonic solfa is a system for understanding the structure of scales and the relationship of the notes inside a scale based on hearing intervals between the notes. It helps learn different scales and key signatures, where the letter names can simply be confusing.
If you feel more comfortable using solfa, make sure to download the fingering chart for the first position with solfa note names here:

Violin First Position Fingering Chart
with Solfa Note Names























